A guide to SOLO for parents, caregivers and whānau

WHAT and WHY
The classroom based use of SOLO is an approach developed by Pam Hook to make learning visible to students, and support them to deepen their learning. SOLO is used to both design learning tasks and assess student learning outcomes. The power of SOLO is that it makes it clear to students where they are at, and what they need to do to their work to show a deeper level of learning. With SOLO the focus is on the complexity of the student response, and how it might be improved, rather than on labelling the student. It is a thoroughly researched and proven teaching approach.

Understanding SOLO levels
When students’ learning is assessed according to SOLO, the learning outcome will be at one of the 5 levels below. Here is a brief explanation of what each level means.
SOLO can either be declarative (describing – usually writing or talking about knowledge) or functional (usually demonstrating a skill).
A simple way of thinking about it is the three Cs:
- Collect: information or skills
- Connect: the information or skills
- Create: make the information or skill your own
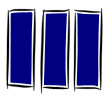
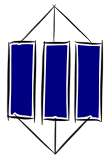
| Collect | Connect | Create | |||
| PRESTRUCTURAL | UNISTRUCTURAL | MULTISTRUCTURAL | RELATIONAL | EXTENDED ABSTRACT | |
 |
 |
 |
|||
| Declarative knowledge | The learning outcome does not answer the task. | The student has one relevant idea. | The student has several relevant ideas. | The student has connected the relevant ideas. | The learning outcome extends the connected ideas, looking at the ideas in a new way. |
| Declarative verbs | define, identify, find, label. | describe, list, find, match. | compare, explain, sequence, classify, link, integrate, analyse, apply, relate, correct, perform, show control. | evaluate, generalise, predict, hypothesise, show insight, create, justify, reflect, prove, show mastery or insight. | |
| Functional knowledge | The student cannot do the skill. | The student can do the skill if helped, or if copies or models someone else. | The student can do the skill, but makes mistakes/cannot do it consistently. | The student can do the skill consistently, and knows when and why to use the skill. | The student can do the skill in a new or improved way. and/or Show others how to do it. |
| Functional verbs: plan, design, select, interview, question, collaborate, reflect, apply, listen, solve, use, mix, measure, observe, throw, share, cut, solder, join, participate in, contribute to, draw, sketch, move, demonstrate etc. | |||||
